Research Advances Disease Diagnostic Technology for ‘Hevea brasiliensis’ Natural Rubber TreesBridgestone Group Works Toward realization of 100% sustainable materials
TOKYO (July 10, 2012) - Bridgestone Corporation today announced that through a NEDO research collaboration project*1 it has developed technologies to improve disease diagnosis for Hevea brasiliensis*2, commonly known as natural rubber trees.
Bridgestone has been focusing resources on the serious problem of white root disease*3, which is plaguing Hevea brasiliensis in Southeast Asia, where more than 90% of the trees are grown. Currently, white root disease is diagnosed through visual analysis, which leads to low detection accuracy and delayed discoveries or misdiagnosis. These shortcomings have permitted the disease to spread widely. Therefore, since 2010, the Bridgestone Group has been working with the Indonesian Agency for the Assessment and Application of Technology and Bogor Agricultural University, Tokyo University of Agriculture, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology, and Kyushu University to jointly promote technologies for diagnosing and preventing the disease under the administration of a NEDO research collaboration project.
This research collaboration has led to the development of four new technologies for early disease detection, namely:
• Pathogen detection based on DNA analysis
• Diagnosis based on latex component analysis
• Diagnosis based on leaf-surface spectral and temperature-measurements
• Regional health diagnosis based on satellite-image analysis
These technologies rely on skills in many scientific fields, including plant pathology, molecular biology, biochemistry, analytical chemistry, and remote sensing. The technologies developed now enable early disease diagnosis using simple tools that do not rely on visual analysis and can quantify pathogen density in the soil.
Looking ahead, the Bridgestone Group will continue working with Indonesian and Japanese universities to advance and share these diagnostic technologies which help protect and strengthen the Hevea brasiliensis species which is essential to ensure a stable, sustainable supply of natural rubber in the future.
Demand for tires is expected to increase in tandem with growth in automobile ownership worldwide. The Bridgestone Group is committed to effectively using the earth's resources as well as the advancement of 'reducing', 'reusing', and 'recycling' initiatives. In addition, the Group believes that in the future new resources for tires should derive from sustainable materials. Therefore, the Group aims to eventually develop tires from 100% sustainable materials*4 through research into biomaterials in several fields, including the research discussed here for enhancing natural rubber productivity.
*1 A project operated by New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO, an
independent administrative agency, it conducts joint research on technology for resolving issues with technological development in developing countries.
*2 Hevea brasiliensis is an evergreen tree native to Brazil that belongs to Euphorbiaceae, Hevea brasiliensis . Emulsion (latex) contains natural rubber, which is obtained by scratching the surface.
*3 White root rot disease (Rigidoporus microporus) is a filamentous bacterium disease that infects Hevea
brasiliensis. It infects roots, killing trees through rotting, and is difficult to detect in its early stages. There are no radically effective remedies. Once onset, chemical treatments are applied after diseased sections are removed.
*4 Materials other than those such as fossil fuel that are expected to be depleted after prolonged use.
The disease and its remedies are outlined below:
1.White root disease
White root disease (Rigidoporus microporus) is a fungal disease that infects Hevea brasiliensis. It infects roots, killing trees through rotting. The infected site sprouts mycelia, and their spores (mushrooms) appear, as seen in the photos.


2.Pathogen detection based on DNA analysis
Using DNA analysis, the technology accurately detects and quantifies white root disease directly from the soil. It can assess infection risks prior to planting.
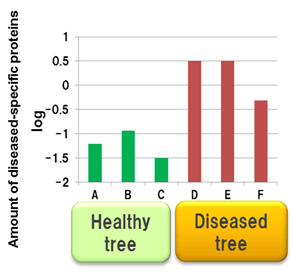
3.Diagnosis based on latex component analysis
The technology is useful for disease diagnoses by latex-component analysis. The disease changes the quantities of some protein components.
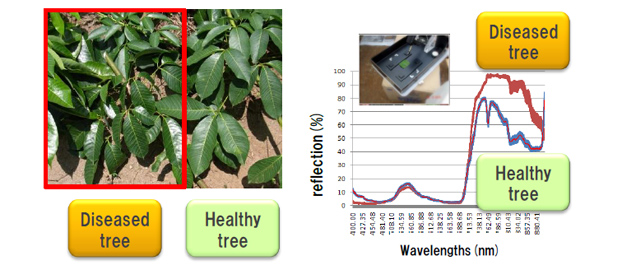
Spectrometers and infrared thermography accurately detect temperature and color changes in trees, enabling more reliable disease diagnosis.
(1)Spectral measurement of leaf-surface
The spectrometer compares reflection rates of diseased and healthy trees.
The diseased trees have higher reflection rates in the near-infrared range.
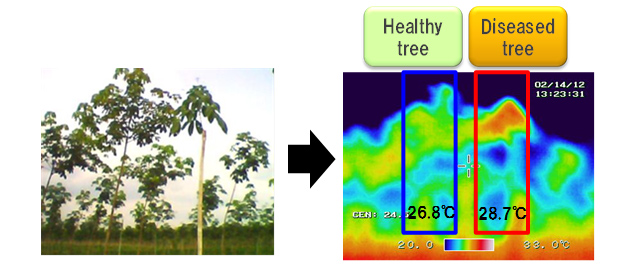
(2)Temperature measurement with infrared camera
In comparison to a healthy tree, the temperature of diseased tree shows higher
temperature value.
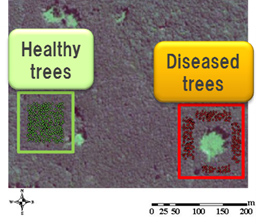
Using remote sensing technology, large plantation areas can be diagnosed, enabling early detection of diseased trees.
The Bridgestone Group plans to refine and optimize the technologies in 2013, and will consider commercializing them for use in fields from 2014.
related link:
·News(May 31,2012)
Bridgestone Corp. and Ajinomoto Co., Inc. Jointly Developing Synthetic Rubber from Biomass
·News(May 23,2012)
Bridgestone Announces Future Tire Technologies that Contribute to a Sustainable Society
·News(May 17,2012)
Bridgestone Finds Russian Dandelion May Be a Sustainable Source of Natural Rubber
·News(Mar 08,2012)
Bridgestone Launches Research Project to Develop a Sustainable Source of Natural Rubber
·Environmental mission statement
About Bridgestone Corporation:
Bridgestone Corporation, headquartered in Tokyo, is the world’s largest tire and rubber company. In addition to tires for use in a wide variety of applications, it also manufactures a broad range of diversified products, which include industrial rubber and chemical products and sporting goods. Its products are sold in over 150 nations and territories around the world.
Bridgestone Corporation, headquartered in Tokyo, is the world’s largest tire and rubber company. In addition to tires for use in a wide variety of applications, it also manufactures a broad range of diversified products, which include industrial rubber and chemical products and sporting goods. Its products are sold in over 150 nations and territories around the world.


